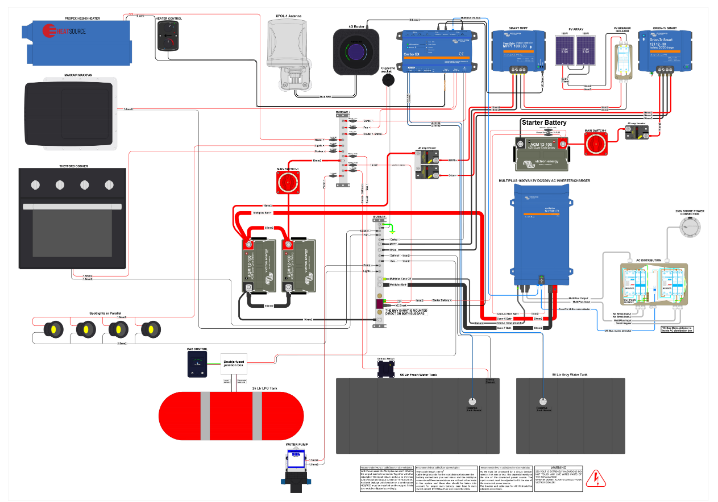
Your RV is a home away from home, and understanding its electrical system is crucial for a safe and enjoyable experience. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into every aspect of RV electrical systems, ensuring you have the knowledge to make informed decisions and keep your RV running smoothly.
Understanding the Basics of RV Electrical Systems
RV electrical systems can be complex, but breaking them down into manageable components makes them easier to understand. There are three main components in any RV electrical system:
- 12-volt DC system: This powers your RV’s lights, water pump, furnace, and other appliances that run on 12-volt power. It’s primarily powered by your RV’s battery bank.
- 120-volt AC system: This supplies power to household appliances like your air conditioner, microwave, and television. It relies on shore power, a generator, or an inverter to provide the necessary electricity.
- Battery bank: The heart of your RV’s electrical system, the battery bank stores and provides power to both the 12-volt DC and 120-volt AC systems.
Understanding these three components and how they interact is essential for maintaining a well-functioning RV electrical system.
Different Types of RV Batteries
Choosing the right battery for your RV is crucial for ensuring your electrical system runs efficiently. There are three main types of RV batteries:
- Flooded Lead-Acid (FLA) Batteries: These are the most common and affordable option. They require regular maintenance, including checking and refilling the electrolyte levels.
- Absorbed Glass Mat (AGM) Batteries: These maintenance-free batteries are sealed, making them more resistant to vibration and offering a longer lifespan than FLA batteries. They’re also more expensive.
- Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) Batteries: The most advanced and expensive option, Li-ion batteries are lightweight, maintenance-free, and have a significantly longer lifespan than other battery types.
When selecting a battery, consider factors such as capacity, weight, maintenance requirements, and cost to find the best fit for your needs.
Charging Your RV Batteries
Keeping your RV’s battery bank charged is essential for a well-functioning electrical system. There are four main ways to charge your batteries:
- Shore power: When connected to an external power source at a campground or RV park, your RV’s converter will charge your battery bank.
- Generator: A portable or built-in generator can provide power to charge your batteries when shore power isn’t available.
- Solar panels: Solar panels can be mounted on your RV’s roof to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity to charge your batteries.
- Alternator charging: While driving, your RV’s engine alternator can charge your battery bank.
Understanding and utilizing these charging methods will ensure your RV’s electrical system remains fully powered.
RV Inverters and Converters
Inverters and converters play crucial roles in your RV’s electrical system:
- Inverters: An inverter converts 12-volt DC power from your RV’s battery bank into 120-volt AC power, enabling you to run household appliances without being connected to shore power or using a generator. There are two types of inverters:
– Modified Sine Wave Inverters: These are more affordable but may not be suitable for sensitive electronics.
– Pure Sine Wave Inverters: These provide clean, consistent power, making them the best choice for sensitive electronics but are more expensive.
- Converters: A converter transforms 120-volt AC power from shore power or a generator into 12-volt DC power, which charges your RV’s battery bank and powers your 12-volt appliances.
Selecting the appropriate inverter and converter for your RV ensures a seamless transition between power sources and keeps your electrical system running smoothly.
RV Solar Power Solutions
Harnessing solar power is an eco-friendly and cost-effective way to charge your RV’s batteries. To set up a solar power system, you’ll need:
- Solar panels: Choose between rigid, flexible, or portable solar panels, depending on your RV’s roof space and your travel preferences.
- Charge controller: This device regulates the flow of electricity from the solar panels to your battery bank, preventing overcharging.
- Inverter: If you want to use solar power for 120-volt AC appliances, you’ll need an inverter to convert the DC power generated by the solar panels.
Solar power systems are scalable and can be customized to meet your specific needs, making them an excellent option for RVers seeking independence from shore power and generators.
RV Electrical Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity of your RV’s electrical system. Follow these tips to keep your system in top condition:
- Inspect and clean battery terminals: Check for corrosion and loose connections, cleaning and tightening as needed.
- Check electrolyte levels: For flooded lead-acid batteries, maintain proper electrolyte levels to prevent damage.
- Test battery capacity: Use a multimeter or battery monitor to check the voltage and capacity of your batteries.
- Inspect and clean power connections: Regularly check power cords, outlets, and connections for signs of wear or damage.
- Exercise your generator: Run your generator monthly for at least 30 minutes to keep it in good working order.
By following these maintenance tips, you’ll ensure your RV’s electrical system remains reliable and efficient.
RV Electrical Safety Precautions
Safety should always be a top priority when dealing with electricity. Follow these safety precautions to prevent accidents and protect your RV’s electrical system:
- Use proper grounding techniques: Always use a grounded power source and surge protector to protect your RV’s electrical components.
- Avoid overloading circuits: Be mindful of the total amperage of your appliances and avoid overloading your RV’s electrical system.
- Inspect power cords and adapters: Regularly check for frayed or damaged cords and replace them as needed.
- Install and test safety devices: Ensure your RV is equipped with functioning smoke alarms, carbon monoxide detectors, and propane detectors.
- Practice safe generator usage: Follow manufacturer guidelines for safe generator operation, including proper ventilation and fuel handling.
By adhering to these safety precautions, you’ll minimize the risk of accidents and ensure the well-being of you and your fellow RVers.
In conclusion, understanding and maintaining your RV’s electrical system is essential for a safe and enjoyable RV experience. By following this comprehensive guide, you’ll be well-equipped to manage your RV’s electrical needs, allowing you to focus on the adventure ahead.
Resources
- The Family Handyman – RV Electrical System Guide: https://www.familyhandyman.com/project/rv-electrical-system-guide/
- Camping World – Understanding RV Electrical Systems: https://blog.campingworld.com/rv-basics/understanding-rv-electrical-systems/
- Go RVing – A Beginner’s Guide to RV Electrical Systems: https://www.gorving.com/blog/beginners-guide-to-rv-electrical-systems/
- RVshare – The Ins and Outs of RV Electrical Systems: https://rvshare.com/blog/the-ins-and-outs-of-rv-electrical-systems/
- Trailer Life – Mastering Your RV’s Electrical System: https://www.trailerlife.com/tech/diy/mastering-your-rvs-electrical-system/
FAQs
- How long does an RV battery last?
The lifespan of an RV battery depends on various factors, such as usage, maintenance, and storage conditions. However, a well-maintained RV battery can last up to six years. - Can I use solar panels to charge my RV battery?
Yes, you can use solar panels to charge your RV battery. Solar panels can be a great alternative to shore power or generators, especially if you’re camping in a remote location with no access to electricity. - How do I know if my RV battery needs to be replaced?
If your RV battery is not holding a charge or if it is more than three years old, it may be time to replace it. You can also have your battery tested to see if it is holding a charge properly. - Can I replace my RV’s electrical system myself?
It is not recommended to replace your RV’s electrical system yourself, as it can be a complicated and potentially dangerous process. It’s best to leave electrical work to a qualified RV technician. - Can I use regular household appliances in my RV?
It depends on the wattage and amperage of the appliance and the capacity of your RV’s electrical system. It’s best to check your RV’s owner manual or consult with a qualified RV technician to determine if your RV can handle the appliances you want to use.